Urban planning plays a pivotal role in shaping the cities we live in today. Urban planning is crucial for creating sustainable cities that prioritize environmental conservation, social equity, and economic prosperity. Urban planners are the architects of our urban environments, tasked with designing livable and environmentally friendly spaces that cater to the needs of diverse populations.

Sustainable Cities
Sustainable cities are the epitome of urban development that harmonizes with nature, society, and the economy. These cities are designed to minimize environmental impact, promote social inclusivity, and drive economic growth. The concept of sustainable cities revolves around the idea of creating urban spaces that are resilient to environmental challenges, provide a high quality of life for residents, and support sustainable economic activities. Key principles of sustainable urban development include efficient land use, resource conservation, sustainable transportation, and green infrastructure.
Environmental Informatics
Environmental informatics is a powerful tool that revolutionizes the way we approach urban planning. It involves the collection, analysis, and interpretation of environmental data using advanced technologies and data science techniques. By leveraging environmental informatics, urban planners can make informed decisions that lead to the creation of sustainable and resilient cities. The significance of environmental informatics lies in its ability to provide real-time data insights, enhance decision-making processes, and optimize resource utilization in urban development projects.
Environmental informatics encompasses a wide range of technologies and methodologies aimed at managing and analyzing environmental data. From Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to remote sensing and data analytics, environmental informatics offers a comprehensive toolkit for urban planners to assess environmental impacts, identify sustainable solutions, and monitor progress towards sustainability goals.
Role of Environmental Informatics in Urban Planning
Environmental informatics plays a crucial role in informing decision-making processes, predicting environmental trends, and optimizing resource allocation. By integrating environmental informatics into urban planning practices, cities can enhance their resilience to climate change, improve air and water quality, and promote sustainable land use practices. Environmental informatics also involves the systematic collection, analysis, and interpretation of environmental data to derive meaningful insights for urban planning. By harnessing the power of data analytics and visualization tools, urban planners can gain a comprehensive understanding of environmental patterns, trends, and challenges, enabling them to make informed decisions that benefit both the environment and the community.
Tools and Technologies of Environmental Informatics
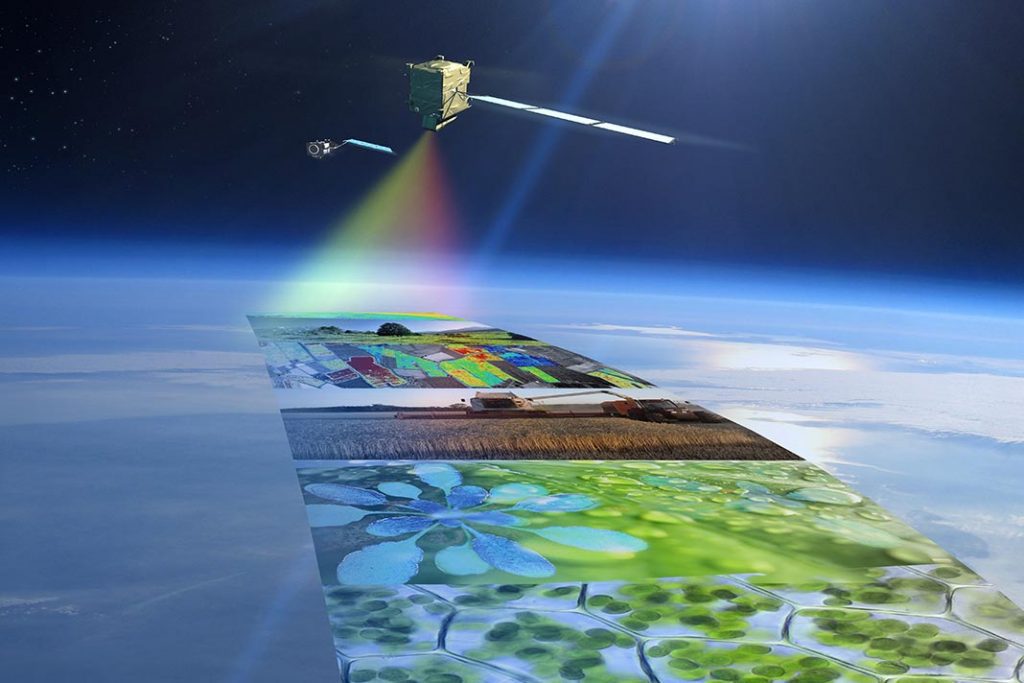
Environmental informatics encompasses a diverse array of tools and technologies that support data collection, analysis, and visualization. From Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to satellite imagery and sensor networks, these tools provide urban planners with valuable insights into environmental conditions, allowing them to design and implement sustainable solutions that benefit both present and future generations.
Incorporating Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in Urban Planning
Incorporating Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in urban planning plays a crucial role in shaping environmentally sustainable urban development by providing planners with enhanced visibility into data, enabling them to monitor fluctuations over time, evaluate project feasibility, and predict environmental impacts. GIS allows planners to integrate diverse data sources seamlessly into one location-based system, combining geographical data with socioeconomic, demographic, and environmental information to make more informed decisions about land use, transportation networks, and environmental impacts. By utilizing GIS technology, urban planners can analyze mobility patterns, optimize transportation routes, assess environmental impacts, and identify suitable areas for development, all contributing to more sustainable and inclusive cities. GIS also facilitates spatial planning, analysis, and modeling, allowing planners to perform complex calculations and modeling for various systems like traffic management, energy distribution, waste management, and infrastructure optimization.
Remote Sensing and Data Analytics for Sustainable Urban Development
Remote sensing is a valuable tool for urban planners to enhance environmentally sustainable urban planning by providing detailed information about various ecological processes shaping the urban environment, such as urban climate, cooling potential, distribution of urban green spaces, and vegetation quality. By utilizing remote sensing data from satellites, airplanes, drones, and handheld devices, urban planners can derive actionable knowledge to support planning decisions in a timely, cost-efficient, and repeatable manner. Remote sensing enables the monitoring of urban evolution at different scales to improve understanding of changes and impacts on urban sustainability, including issues related to urban expansion and sustainable development. It also facilitates the detection and mapping of features and changes on land surfaces that affect urban sustainability, contributing to more informed decision-making in urban planning. The integration of remote sensing data allows for effective extraction of urban features, modeling of urban environments as complex systems, and improved accuracy in classification algorithms for addressing spectral issues in sustainable urban development.

Case Study: Copenhagen
Copenhagen has utilized Environmental Informatics in shaping sustainable urban planning by integrating various approaches and processes at all stages of design, construction, and management. The city emphasizes the prudent use of resources like green spaces, water, land, and air, while encouraging investments in technological innovation and smart technology. Copenhagen’s sustainable urban development includes projects like Nordhavn, a climate-resilient neighborhood with green spaces and clean harbors, showcasing how urban planning combines climate solutions with recreational benefits. Additionally, Copenhagen’s focus on biking as a primary mode of transportation contributes to its sustainability efforts, with designated bike lanes throughout the city and a high percentage of commuters using bicycles. The city is also home to the world’s most sustainable housing project, the UN17 Village in Ørestad, which aligns with all 17 of the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals. Furthermore, Copenhagen has taken a leading role in environmental sustainability through public-private partnerships and initiatives like the Copenhagen Science City, promoting innovative solutions for a greener future.
Outcomes and Impact of Environmental Informatics in Sustainable Urban Development
The outcomes and impact of environmental informatics in sustainable urban development are profound. By harnessing the power of data and technology, cities can enhance environmental sustainability, improve public health, and boost economic growth. The integration of environmental informatics in urban planning leads to more efficient resource management, reduced carbon emissions, and enhanced quality of life for residents.
Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges in Implementing Environmental Informatics in Urban Planning
Despite its numerous benefits, the integration of environmental informatics in urban planning poses several challenges. These include data privacy concerns, technological barriers, and the need for specialized skills and expertise. Overcoming these challenges requires a collaborative effort between government agencies, technology providers, and urban planners to ensure the effective and ethical use of environmental data for sustainable urban development.
Opportunities for Innovation and Improvement in Leveraging Informatics for Sustainability
Amidst the challenges lie opportunities for innovation and improvement in leveraging environmental informatics for sustainability. By fostering collaboration, investing in research and development, and promoting data-driven decision-making, cities can unlock the full potential of environmental informatics to create greener, smarter, and more sustainable urban spaces. These opportunities pave the way for creative solutions, new technologies, and enhanced partnerships that drive the evolution of urban planning towards a more sustainable future.

Future Trends
Emerging Trends in Environmental Informatics for Urban Planning
The future of environmental informatics in urban planning is marked by emerging trends that shape the way cities approach sustainability and resilience. From the integration of Artificial Intelligence for environmental monitoring to the use of big data technologies for environmental insights, cities are embracing innovative solutions that leverage data and technology to address complex environmental challenges. These trends reflect a shift towards data-driven decision-making, digital transformation, and sustainability-driven urban development practices.
Influence of Technology and Data Science on Sustainable City Design and Management
Technology and data science have a profound influence on sustainable city design and management. By harnessing the power of environmental informatics, cities can optimize resource allocation, enhance environmental monitoring, and improve infrastructure planning. The integration of technology and data science into urban planning processes empowers cities to make informed decisions that promote sustainability, resilience, and long-term prosperity for residents and the environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the integration of environmental informatics in urban planning is essential for shaping sustainable and resilient cities of the future. By leveraging advanced tools and technologies, urban planners can design environmentally friendly spaces, optimize resource management, and enhance the overall quality of urban living. As we look towards a greener and more sustainable future, it is imperative to continue researching and implementing environmental informatics in urban planning to create cities that are not only technologically advanced but also environmentally conscious and socially inclusive.
Summary of the Importance of Integrating Environmental Informatics in Urban Planning for Sustainable and Resilient Cities
The role of environmental informatics in shaping sustainable urban planning cannot be overstated. By integrating data-driven approaches and advanced technologies, cities can address environmental challenges, promote sustainable development, and enhance the quality of urban life. The integration of environmental informatics is key to creating cities that are resilient to climate change, resource-efficient, and socially inclusive.
Call to Action for Continued Research and Implementation of Environmental Informatics in Urban Planning for a Greener Future
By embracing innovation, fostering collaboration, and adopting data-driven decision-making, cities can unlock the full potential of environmental informatics to create sustainable and resilient urban spaces. Together, we can build a greener future for generations to come, where technology and environmental conservation coexist harmoniously to create cities that are not only sustainable but also vibrant, inclusive, and prosperous.
| Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|
| 1. Facilitates data-driven decision-making | 1. Data privacy concerns |
| 2. Enhances resource optimization | 2. Technological barriers |
| 3. Improves environmental monitoring and analysis | 3. Need for specialized skills and expertise |
| 4. Supports evidence-based sustainable development |